
Back ممر قانسو Arabic Corredor del Hexi AST Хъси Bulgarian Corredor de Hexi Catalan Kansuský koridor Czech Hexi-Korridor German Hesi-koridoro Esperanto Corredor del Hexi Spanish Hexi korridorea Basque Corridor du Hexi French
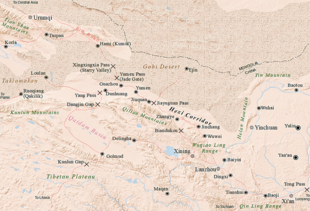
The Hexi Corridor (Chinese: 河西走廊; pinyin: Héxī Zǒuláng; Wade–Giles: Ho2-hsi1 Tsou3-lang2, Xiao'erjing: حْسِ ظِوْلاْ, Mandarin pronunciation: [xɤ˧˥ɕi˥ tsoʊ˨˩˦lɑŋ˧˥]), also known as the Gansu Corridor, is an important historical region located in the modern western Gansu province of China. It refers to a narrow stretch of traversable and relatively arable plain west of the Yellow River's Ordos Loop (hence the name Hexi, meaning "west of the river"), flanked between the much more elevated and inhospitable terrains of the Mongolian and Tibetan Plateaus.
As part of the Northern Silk Road, running northwest from the western section of the Ordos Loop between Yinchuan and Lanzhou, the Hexi Corridor was the most important trade route in Northwest China. It linked China proper to the historic Western Regions for traders and military incursions into Central Asia. It is a string of oases along the northern edges of the Qilian Mountains and Altyn-Tagh, with the high and desolate Tibetan Plateau further to the south. To the north are the Longshou, Heli and Mazong Mountains separating it from the arid Badain Jaran Desert, Gobi Desert and the cold steppes of the Mongolian Plateau. At the western end, the route splits into three, going either north of the Tianshan Mountains or south on either side of the Tarim Basin. At the eastern end, the mountains around Lanzhou grants access to the Longxi Basin, which leads east through Mount Long along the Wei River valley into the populous Guanzhong Plain, and then into the Central Plain.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search